Common data elements.
Understanding common data elements and data harmonization.
-
A Common Data Element (CDE) is a standardized definition used to describe the meaning of a variable in a dataset. CDEs are typically grounded in established ontologies such as SNOMED, LOINC, or the NCI Thesaurus, and they specify both what a data element represents and which values it may take. By reducing ambiguity, CDEs support consistent data collection and enable reliable comparison and reuse across studies and data resources.
For example, MIDRC includes a property called “race” within the patient (“case”) node. Even with a written definition, data collectors and researchers may interpret this variable differently. To address this, the MIDRC data model links the property to NCI Thesaurus code C17049, which precisely defines the concept and its allowable values. Without such standards, information might be recorded inconsistently—for example, by relying on observation, patient self-description, or by conflating race with ethnicity, which MIDRC defines separately using NCIt code C16564.
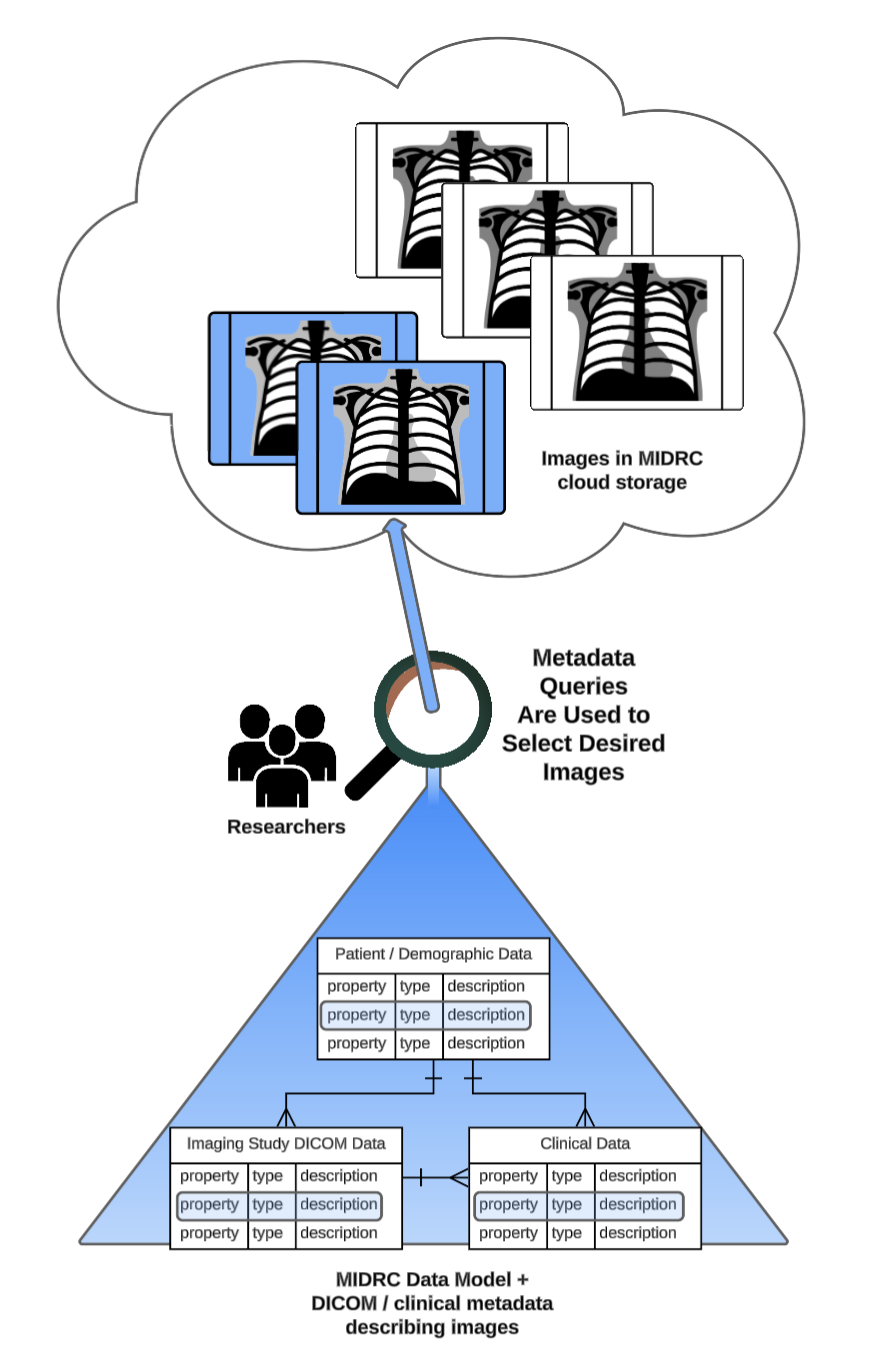
MIDRC uses CDEs throughout its data model to standardize properties and acceptable values so that data are ingested consistently across sites and datasets. This standardization also allows researchers to confidently combine MIDRC data with other repositories that use the same or related CDEs.
It is worth noting that “CDE” can also refer to a Common Data Environment, a centralized platform for storing, managing, and sharing project data with features such as version control, access permissions, and audit trails. Resources such as the MIDRC Data Commons function in this way; however, MIDRC primarily uses the term “data commons” in this context and reserves “CDE” to mean Common Data Element.
-
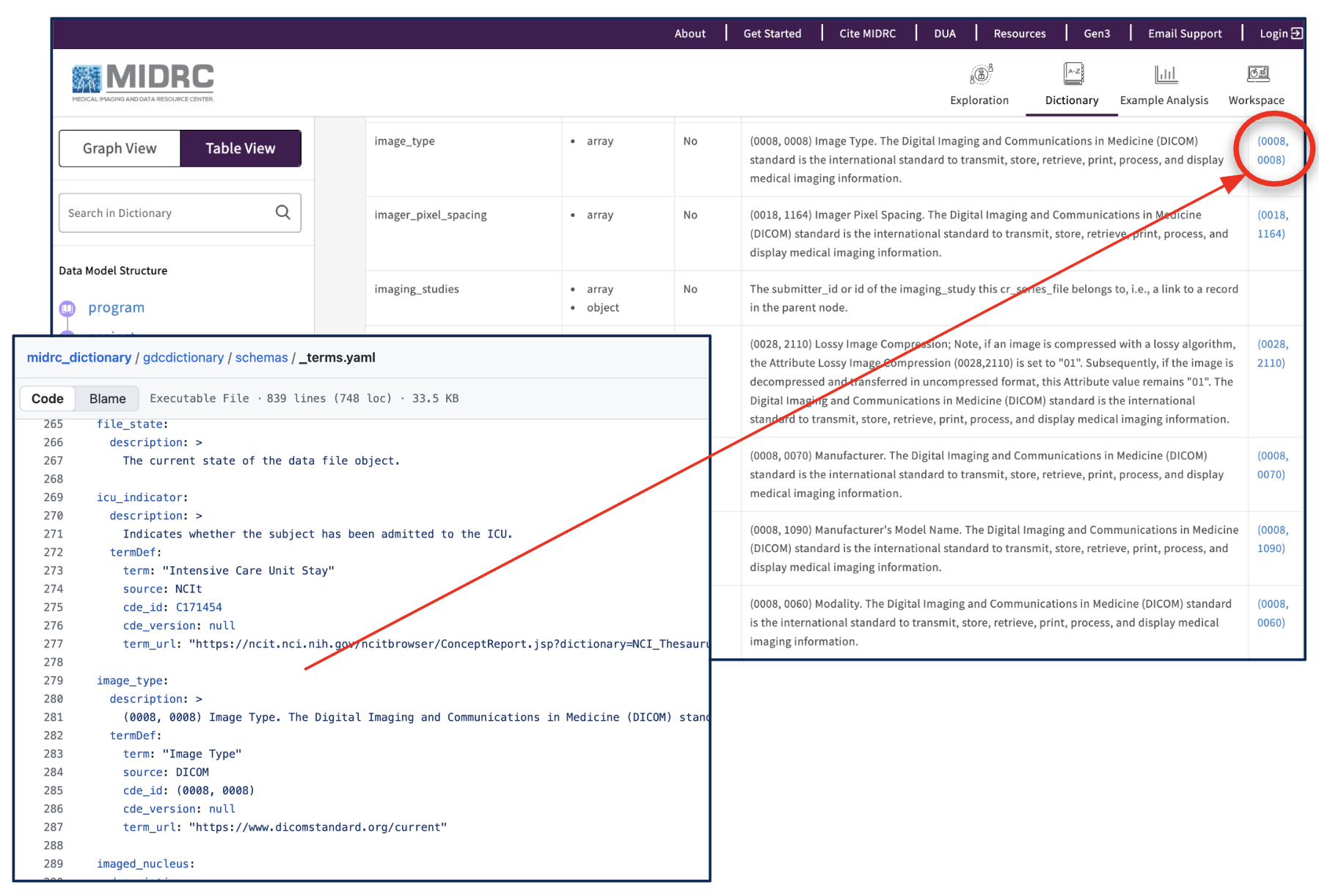
Many MIDRC properties reference CDEs from existing standards and are listed in the data model’s “_terms” section and table view. Some properties, however, are unique to MIDRC and may not yet have an external standard. MIDRC subcommittees continue to align these elements with third-party ontologies so users can more easily interpret and reuse the data.
Learn more about MIDRC CDEs:
https://data.midrc.org/DD
https://github.com/MIDRC/midrc_dictionary/blob/master/gdcdictionary/schemas/_terms.yamlMIDRC has also worked with the National Library of Medicine to request new standard CDEs for properties that lacked suitable existing terms, contributing to broader data standardization efforts.
Learn more about the NIH CDE Repository:
https://cde.nlm.nih.gov/home -
Although DICOM is the standard for medical imaging, it does not enforce controlled vocabularies for many tag values. As a result, entries such as Study Description or Body Part Examined may vary by institution, equipment, or operator, making cohort selection challenging when relying on raw values alone.
To address this, MIDRC harmonizes imaging study data using LOINC. Frequently occurring combinations of Study Description and Modality are mapped to LOINC codes, which in turn define standardized concepts such as body system, contrast use, modality, and study description. These harmonized terms serve as filters in MIDRC’s Data Explorer, allowing researchers to identify comparable imaging studies even when the original DICOM entries differ.
Currently, the majority of MIDRC imaging studies have been mapped from thousands of original study descriptions to a much smaller set of LOINC codes, substantially improving searchability and cohort building.
-
During data intake, raw DICOM headers and associated clinical data are extracted, structured according to the data model, and ingested into the MIDRC data commons. Derived properties are then calculated, and imaging study data are harmonized to LOINC terms. MIDRC teams regularly review frequently occurring unmapped study descriptions and map them to appropriate codes, supporting ongoing improvements in data consistency.
-
Harmonization increases data reuse and strengthens interoperability between MIDRC and other research resources. By aligning data elements with shared standards, researchers can more efficiently discover relevant data, build cohorts, and conduct analyses across datasets collected by different institutions and initiatives.
Learn more about the HEAL Common Data Elements Repository:
https://heal.nih.gov/data/common-data-elements-repository
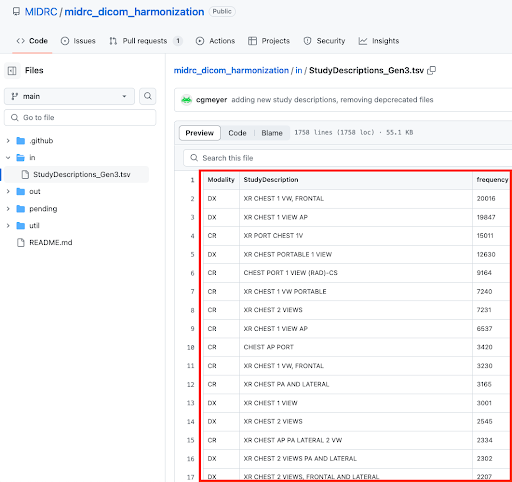
Before harmonization: Raw input for the LOINC harmonization process, which is a list of Modality and Study Description combinations sorted by their frequency of occurrence in MIDRC data.
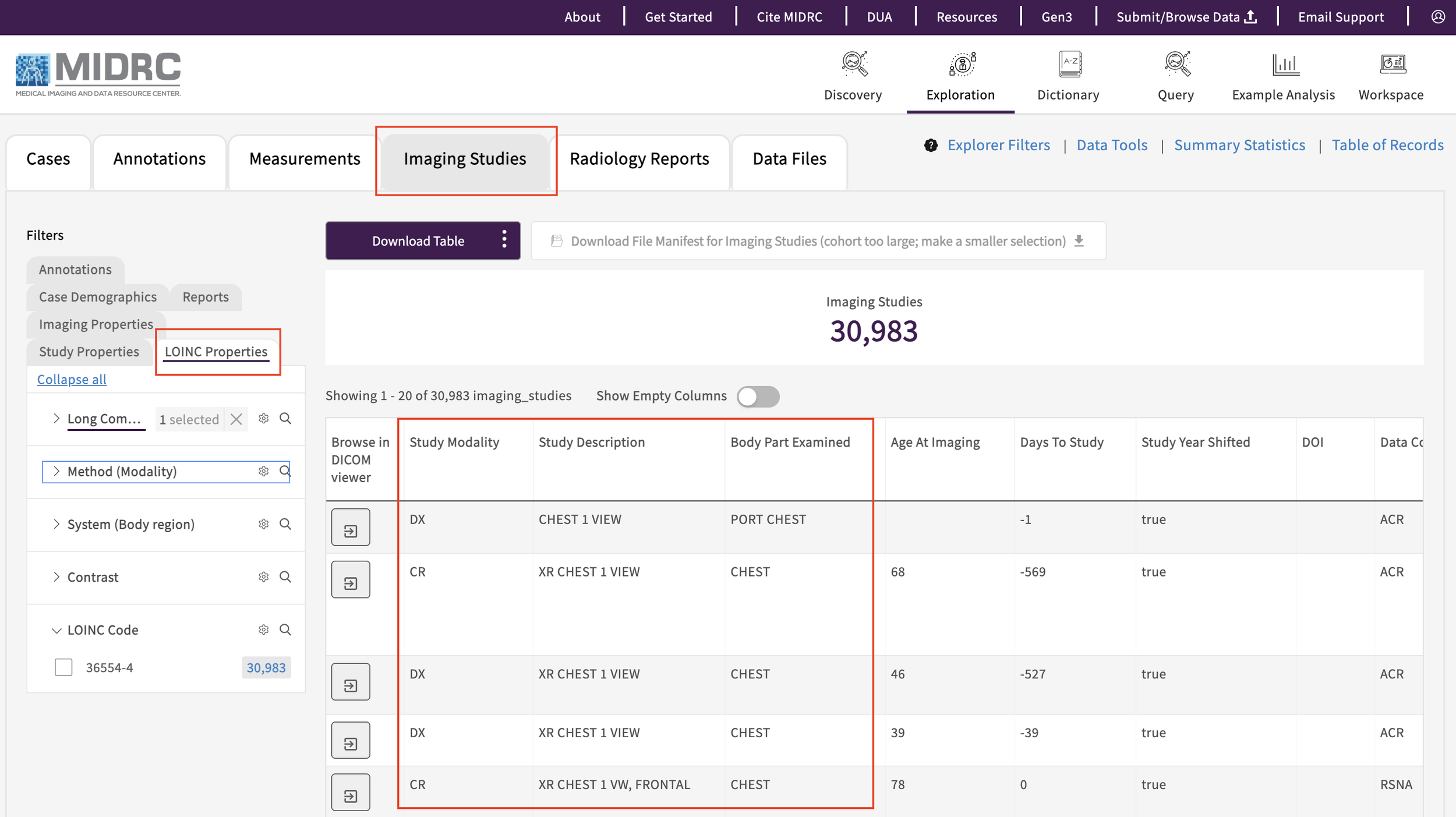
After harmonization: The LOINC filters on the MIDRC data explorer’s “Imaging Studies” tab, which enables users to select imaging studies based on harmonized Study Description, Modality, Body Part Examined, and Contrast values.
Terms in the MIDRC data model, which point to third-party standard ontologies where common data elements are defined outside of MIDRC.
Last updated January 30, 2026