MIDRC in a nutshell.
The Medical Imaging Data Resource Center (MIDRC; https://midrc.org) was launched in 2020 to accelerate medical machine learning research. It is primarily funded by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), with additional support from other partners, and is hosted at the University of Chicago. MIDRC is co-led by the American College of Radiology (ACR), Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), and American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM).
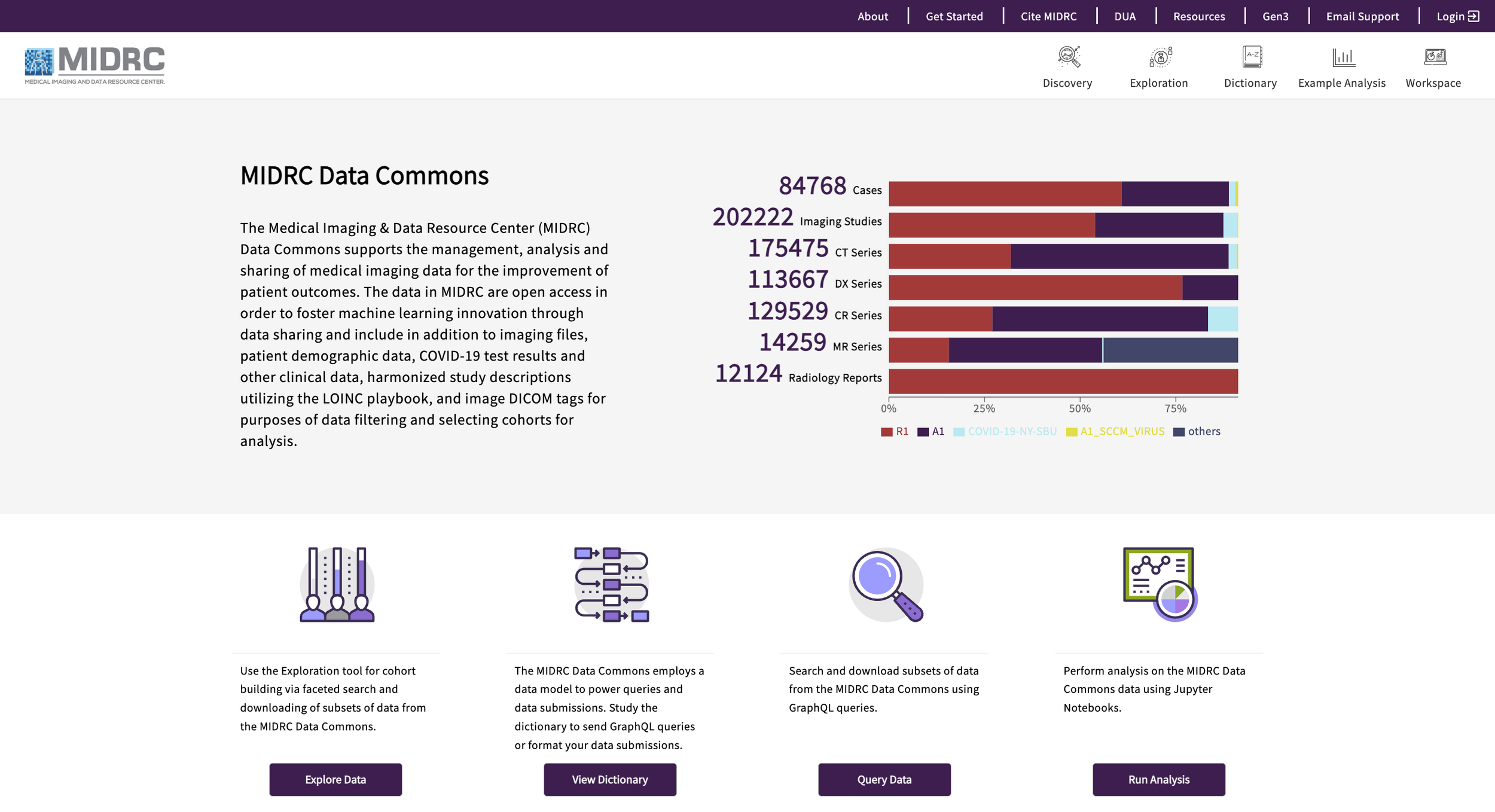
MIDRC maintains a curated data commons that co-locates de-identified medical images with associated clinical data, expert annotations, radiology reports, and tools for data discovery and analysis. Although the initiative began with COVID-19-related studies, it has expanded to include diseases such as cancer, traumatic brain injury, and fibrosis. All data are de-identified prior to inclusion.
Eighty percent of incoming data are allocated to the open commons for researcher access and machine learning (ML) development, while the remaining twenty percent are sequestered into a private validation set to support regulatory evaluation of AI models. These datasets are balanced with respect to DICOM and demographic data elements using a stratified sampling algorithm (Baughn et al., 2023).
The MIDRC Data Commons, powered by the open-source Gen3 platform, supports findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR) data. Users can discover datasets, build cohorts, and access data through integrated analysis tools, notebooks, and workspaces.
MIDRC also interoperates with other data commons through the BDF Imaging Hub, which indexes external imaging datasets to enable cross-commons cohort discovery. After defining a cohort, users download the data directly from the respective data commons.